- Sep 14, 2021 Packet Sniffer Mac Os X; Packet Sniffer For Mac Installer; If you have more than one workstation, you administer several machines connected to a network, or just frequently connect to various networks, sooner or later you’ll find a packet sniffer to be quite useful. Packet Peeper is a free network protocol analyzer (or ‘packet sniffer.
- Capsa Free is a network analyzer freeware for Ethernet monitoring, troubleshooting and analysis. It provides users with great experience to learn how to monitor network activities, pinpoint network problems, enhance network security. Capsa Free is a special edition of Capsa Network Analyzer for students, teachers and computer geeks to learn.
A network sniffer, or packet sniffer, is a specialized software (or even a hardware device) that listens in over a network and records the IP packets of data that travel through it.
Dec 13, 2020 Description. Download Sniffer 1.1.0 for Mac from our website for free. Our antivirus scan shows that this Mac download is clean. The actual developer of this free software for Mac is mmmooo. Sniffer for Mac belongs to Education Tools. The most popular version of the software is 1.1. This app is smart in capture; smart to deliver noise level for.
Many network administrators use these tools to determine the efficiency of a network, to troubleshoot communication problems, to identify common network bottlenecks etc.
Of course, hackers can also use network sniffing tools to collect personal data such as passwords over a network. That’s why network traffic should be encrypted wherever possible.
As a network and security engineer I have been using network sniffing tools for decades. The easiest way to collect network traffic with a sniffing tool is to connect your computer (which has the sniffer software installed) on a SPAN port of a switch which basically copies all traffic passing through the switch to that SPAN port.
The sniffing software is listening on the network interface card of the computer to collect all traffic which passes through the interface for analysis. Of course, this is one way of capturing network traffic. There are more options as we’ll see below.
In this article I have researched some popular (both free and commercial) IP network sniffing tools and present them below with a brief description of each one.
The ranking below is in no particular order:
Table of Contents
1) WireShark – FREE
As one of the world’s most used network sniffing and analysis tools, WireShark has a wealth of features that are continually being added to by a community of volunteers.
This free tool is usually the de-facto first option for network and system engineers for capturing and analyzing network packets.
WireShark is available across various platforms, including Windows, Mac, Linux, FreeBSD, Solaris, and others. It also can read hundreds of network protocols and can do all of this in real time over a variety of networks, including Ethernet, PPP, Bluetooth, FDDI etc.
A website full of information with a wealth of tutorials and documents tops all of this off, and they even conduct regular training on how to use their software.
This makes it relatively easy to get up to speed on not just how to use the tool, but also how it can help network administrators and other IT professionals improve the speed and efficiency of their networks.
Personally I use Wireshark extensively in my work environment to either troubleshoot problems or inspect traffic for security purposes.
There is a learning curve to find out the various filters needed to apply in order to search within packets and display only the packets you want. If you learn these, the tool is very powerful and flexible.
2) PRTG IP Sniffer – PAID
PRTG by Paessler is a popular and powerful network monitor tool which does much more than IP sniffing.
PRTG’s approach to network monitoring is based on sensors. You can set up sensors across an entire network that measure the values of different things such as CPU load, disk space, bandwidth and so on.
Once you set them up, they can all be monitored from a central dashboard. In this sense, the sensors act like little network alarms that will alert the network administrator to a network problem.
There’s a lot to like about this approach, and the first 100 sensors are free to use for 30 days, after which the software will revert to a free version that has limitations. The unique sensor-based approach that PRTG takes makes it an interesting choice.
Now, the IP Sniffing functionality of PRTG is another sensor just like the other ones they have.
The Packet Sniffer Sensor uses a built-in packet sniffer to monitor the headers of data packets passing through the network card. Only packet headers are captured.
3) Solarwinds Deep Packet Inspection – PAID
Solarwinds is another big player in the network management/monitoring arena. They develop tools for all sorts of management tasks, monitoring, analysis of IT infrastructure etc.
If you want to see where your data bottlenecks are located across a sophisticated network, the Solarwinds Deep Packet Inspection tool offers some unique insights.
By presenting all information in an easy to read and interpret graphing front-end, Solarwinds is ideal for those who need to know everything about their network and how it performs under load.
Out of the box, Solarwinds has support for analyzing the network traffic for 1200 applications. Such applications include Skype, SQL server, Social Media traffic, Web Traffic and many more.
The Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) tool classifies traffic into categories. A business can use this classification to identify traffic that is not business-related (e.g excessive social media traffic) in order to apply rate limiting, traffic blocking etc.
4) Tcpdump – FREE
If you’re more accustomed to command line applications and need something fast and powerful, Tcpdump is one of the best choices available in the world of packet sniffing and analysis in the Unix world.
This software is ideal for Linux-based machine and gives you the ability to capture packets going in and out of the host’s network card and presents the results in printed format for easy reading and analysis.
As with many command line applications, many features can be controlled with flag settings. Tcpdump is very powerful and flexible but is more geared towards system admins with some Linux knowledge.
5) WinDump – FREE
Windump is the Windows version of the above mentioned tcpdump. It also presents information in a command line interface and is compatible with tcpdump.
Just like tcpdump, Windump is free and is made for those who like a simple but powerful command line-driven experience for deep packet troubleshooting across a host.
It is based on the free WinPcap which is a driver for capturing packets form the host’s network interface.
6) Manage Engine Netflow Analyzer – PAID
This real time network analysis tool uses an attractive graphical interface to display traffic data over a network.
It is based on packet flow technologies and supports Cisco’s Netflow, Juniper’s JFlow, sFlow, IPFix, Appflow and Netstream.
Using the above Flow Technologies, this software is ideal for people who want to be able to visualize everything in real time and drill down on the details to identify any potential network issues.
It supports major hardware vendors such as Cisco and HP, and can display data from all supported hardware devices using Flow Technology.
This is an easy way to see where there might be any network problems. Color-coded pie charts and summarized information on a single screen make this a wise choice for professional network administrators. Contoh rab coffee shop.
The Manage Engine tool works as a collector to receive flow traffic from network devices such as routers, switches etc and any other device that can send flow data. This allows it to monitor bandwidth usage, application usage, security monitoring etc.
7) EtherApe – FREE
This may not be the most complex or complete tool available, but for those who rely on Unix, this GTK3-based network monitor can get the job done.
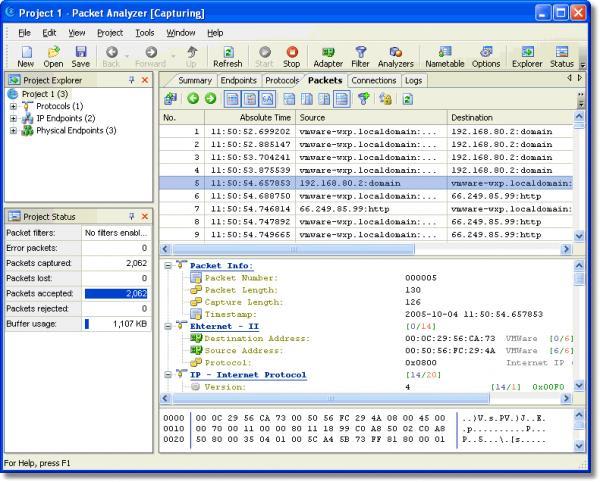
It uses an easy to decipher color-coded display for visualizing network and packet data, and has RPM packages that have been built for Arch Linux, Fedora, OpenSUSE, and Mageia 6.
The use of the GTK3 graphical libraries make this an attractive native Linux experience in several flavors.
The display of network data is heavily graphical and intuitive in design, with more active nodes appearing large on the screen.
This makes an otherwise arcane tool rather easy to use and interpret, even for those with intermediate knowledge of networks.
8) LiveAction Omnipeek – PAID
Though not free, this network analyzer offers professionals a powerful and intuitive way to view network congestion, identify problems, and focus on solving Wi-Fi speed issues among others.
Many network tools have a distinct focus on traditional wired networks, but Omnipeek provides a sophisticated way to visualize the data flow within wireless networks as well. This makes it thoroughly up to the job in the modern world, where wireless networks are very common.
Moreover, it helps admins to troubleshoot and monitor Voice and Video traffic, end-user devices, and also decode over 1000 protocols.
The solution offers also an appliance option (LiveCapture) used to distribute the collection and network monitoring at remote sites and branches.
9) Netresec Network Miner – FREE or PAID
Coming in both a free and professional paid version, Netresec Network Miner is an open source software tool that features a passive mode operation.
Operating in this mode ensures that no extra load is placed on the network, and Network Miner goes to work capturing packet data and identifying hostname and operating system information.
The featured passive mode makes it an ideal tool for large networks, especially the professional edition, which features many more functions, including exportable reports and OS fingerprinting.
10) Steelcentral Packet Analyzer – PAID
An attractive and intuitive interface is one of the characteristics of this tool.
This makes it quite easy to diagnose problems and bottlenecks across a network. What makes it even easier to use is the included preset analysis views.
By applying one of these preset views, it’s possible to see a wide range of problems presented in an attractive and humanly readable way.
Steelcentral Packet Analyzer makes it a cinch to diagnose issues on large networks in a business environment. It has been designed from the ground up to collect information and present it in a way that speeds up the job of network administrators.
11) Capsa – PAID
Though not inexpensive, Capsa offers numerous features that set it above many other network analysis tools. It is aimed at enterprise environments and operates on a very large scale, delivering information in an easy to read window and dashboard view.
Capsa is extensive, and supports over 1800 network protocols. It’s possible to monitor networks on a 24/7 basis, capture information from multiple networks in real time, and capture instant messaging and email traffic so network administrators are aware of any policy breaches in a business environment.
Conclusion
Network sniffing and analysis tools cover a wide range of functions and needs, and are available in free and paid versions.
The simplest will certainly do the job of capturing data over a network, but for large corporate environments and sophisticated networks, the paid professional offerings are a better option.
Related Posts
In IT operations, ensuring secure and reliablecommunications over different networks is a crucial requirement. ITadministrators have to rely on different protocols, networking best practices,and network monitoring tools to ensure the flow of data in a network meetsvarious standards for security and Quality of Service (QoS). One of thesecommon practices is known as packet sniffing, which helps IT administratorskeep track of packets (small formatted units of data) and ensure they’retransferred smoothly. While the packet sniffing technique is often associatedwith cyberattacks, it’s commonly used by internet service providers, governmentagencies, advertisers, and even large organizations for network monitoring. Inthis article, we’ll discuss packet sniffing in detail and also explore commonlyused tools by IT practitioners.
What Are Packets, and Why Do WeNeed Packet Sniffers?
All networks consist of several components,such as workstations, servers, networking hardware, and more. In the networkingterminology, all these components are called nodes. A healthy networkconnection ensures the data between these nodes is transferred reliably and atan acceptable speed according to the bandwidth and throughput of the network.While most of the traditional networks maintain physical or wired connections,modern networks are a mix of physical and wireless connections. However, theconcepts of data transfer in all such networks remain the same.
In networking, the data is transferred in theform of packets, or small chunks of data. Bluestacks 1 for low end pc. These packets vary in their format,depending on the network protocol (TCP/IP, UDP, etc.). In addition to theactual information or data, all packets contain control information designed tohelp in the delivery of packets from source to destination. The controlinformation is required as packets intended to be transferred to a specificnode often pass through several nodes in a network and can end up at the wrongnode. The control information includes IP addresses of the sender and thereceiver, packet sequencing information (e.g., packet number), and more toensure packets reach the right destination. However, the transfer of packets ina network can get disrupted due to several issues and network errors.
In protocols like TCP/IP, there’s no inherentmechanism to recover the packets lost in transmission. However, networkarchitects use the protocol in only fault-tolerant networks, where losses belowcertain thresholds are acceptable and don’t affect the communication. However,in protocols like UDP, the sender continues to resend the packet until itreceives the acknowledgment of receipt from the receiver. While it addsreliability to the transmission, it also increases resource consumption. Ifleft unchecked, it can lead to significant delays in overall transmissionrates. This is where packet sniffers offer a solution.
With a packet sniffer, sometimes also calledpacket analyzer, network administrators can monitor their network traffic andgain valuable insights about their infrastructure and its performance. Itallows them to measure the traffic flow in a network and also identify whichapplications are using the maximum bandwidth.
How Do Packet Sniffers Work?
As discussed above, when a sender transmitsdata packets, the packets pass through several nodes in a network. Each networkadapter and the connected device examines a packet’s control information to seewhat node the packet is headed toward. Under normal circumstances, if a nodefinds the packet is addressed to some other node, it drops or ignores thepacket. However, in packet sniffing, certain nodes are programmed to not followthis standard practice and collect all or a defined sample of packets,irrespective of their destination address. The packet sniffers use thesepackets for the analysis of a network.
Depending on who’s using the packet sniffers,it can have both positive and negative use cases. Threat actors can extractcritical information from unencrypted messages. Many times users logging intowebsites over unencrypted transmission expose their credentials (user ids,passwords, etc.) in plain text, which can be easily intercepted by packetsniffers. However, packet sniffing also offers many benefits we’ll discusslater in this article.
Types of Packet Sniffers
There are two major types of packet sniffers:
Hardware Packet Sniffers
Free Packet Sniffer Mac Os
As the name suggests, it’s a hardwarecomponent plugged into a network for packet sniffing or network analysispurposes. Hardware packet sniffers are commonly used when networkadministrators have to analyze or monitor a particular segment of a largenetwork. With a physical connection, these packet sniffers allow administratorsto ensure all packets are captured without any loss due to routing, filtering,or any other network issue. A hardware packet sniffer can have the facility tostore the packets, or they can be programmed to forward all captured packers toa centralized location for further analysis.
Software Packet Sniffers
Software Packet Sniffers are the more commontype of packet sniffers used by many organizations. Every computer or nodeconnects to the network using a Network Interface Card (NIC), which isgenerally configured to ignore the packets not addressed to it. However, aSoftware Packet Sniffer changes this behavior, so one can receive every bit ofnetwork traffic for analysis. The NIC configuration is known as promiscuousmode. The amount of information collected depends on whether the packet snifferis set on filtered or unfiltered mode.
Depending on the size and complexity of anetwork, multiple packet sniffers might be required to monitor and analyze anetwork effectively. This is because a network adapter can only collect trafficfrom one side of a switch or a router. Similarly, in wireless networks, mostnetwork adapters can connect to only a single channel at a given time. Tocapture packets from other channels, one has to install multiple packetsniffers.
Top 5 Benefits of Packet Sniffing
1. Detecting the Root Cause of a Network Issue
Today, in most enterprise networks, there areseveral user groups and applications, along with a complex mix of legacy andnext-gen networking equipment. Ensuring all applications and servers performwithout any performance bottlenecks is a huge undertaking. When an applicationor a service experiences an issue, it can be a difficult task to identify whichnetwork or application component is responsible for the slowdown. This is whynetwork administrators monitor their network continuously for routine maintenanceand optimization. With packet sniffers, they can collect information from allpoints of their network to quickly identify the components responsible forlatency, jitters, or packet loss.
2. Troubleshooting Network Issues
Whenever IT teams receive tickets related tonetwork connectivity, they can perform PCAP analysis to measure the responsetimes or latency in a network. It helps in determining the amount of time apacket takes to travel from a sender to a receiver. With this analysis, teamscan identify congested links, detect the applications generating an unusualamount of traffic, and take remedial actions to resolve the issue. Using modernWi-Fi packet sniffers, teams can get performance metrics for different accesspoints and wireless controllers. Many advanced network monitoring tools offeradditional features for fault, performance, and network availabilitymonitoring. It’s also possible to correlate network data across the stack andperform hop-by-hop network path analysis to troubleshoot network issues andminimize network downtime.
3. Traffic Analysis
IT teams can also collect the packet data forpredictive analysis. They can visualize this data to detect the peaks andtroughs in network demand over longer periods. Using advanced IP sniffers andpacket analyzers, they can categorize the data based on destination server IPaddresses, ports involved in communication, the volume of traffic, and more.With all this analysis, it’s possible to distinguish critical traffic (requiredfor VOIP, ERP suites, CRMs, etc.) from non-business traffic (social media,unauthorized messengers, etc.). Also, IT administrators can filter and flagsuspicious content.
4. Bandwidth Management
Slow or intermittent networks can significantly impact business productivity and lead to huge losses. Businesses rely on advanced network monitoring tools to avoid such issues. However, most of these tools also rely on packet sniffing to analyze the traffic in a network. Packet sniffers help in preventing the misuse of the network by both internal and external users. As discussed above, with traffic analysis, IT teams can easily identify the traffic flow and WAN bandwidth utilization, any irregular increase in network usage, and more. Equipped with this data, they can prioritize bandwidth allocation for mission-critical applications, and even restrict certain applications.
5. Network Security and Compliance
It’s not rare for threat actors to infiltratean enterprise network and compromise sensitive data. However, their activitiescan also remain hidden for a long period, and many times they use advancedmalware to make malicious use of enterprise resources. Regular traffic analysisallows the detection of any suspicious increase in outbound traffic flow.Packet sniffers help in detecting a surge in traffic, attempts at networkintrusion, and enable deeper evaluation and mitigation of security threats.They help in checking the status of WAN and endpoint security systems. Packetsniffers also help in regulatory compliance documentation by logging all of theperimeter and endpoint traffic. Moreover, with packet sniffers, security teamscan verify the effectiveness of their security setup consisting of severalfirewalls, web filters, WAF, IPS/IDS systems, and more.
Best Practices for PacketSniffing
Free Packet Sniffer For Mac
There are many network monitoring tools offeringpacket sniffing features. You can also find several open-source applicationsfor packet sniffing. It’s possible to select one of these packet sniffers, setthe NIC to promiscuous mode, and start capturing packets from a network.However, before jumping into action, you must understand how to make the mostof packet sniffing techniques, without compromising your network. Here are someof the best practices for getting started:
Understand Your MonitoringRequirements
While various network monitoring tasks areautomated today, IT practitioners still rely on heuristics and manual analysisto detect issues and resolve network problems. A strong understanding ofnetworking concepts is essential for network monitoring. When using a packetsniffer, experienced teams often opt for the filtered mode to capture only thespecific information from the packets. Collecting all packet data and notknowing what information is crucial for analysis can lead to informationoverload.
Bolster Security
All packets contain control information (e.g.,source and destination IPs) and the actual data or payload during the datatransmission. It’s important to ensure the payload is encrypted during all datatransfers, as packet sniffers can also capture this data, and any sensitiveinformation can inadvertently get exposed if encryption isn’t in place. As anadded layer of security, IT teams can configure their packet sniffers to copyonly the header data as it’s sufficient for most of the network monitoring andanalytics.
Implement Packet Sampling
While restricting the packet sniffing topacket headers reduces workload and storage requirements, it can still lead toa large volume of data and fill up disk space quickly. Packet sampling can helpin resolving this challenge. Instead of collecting data from every packet, ITteams can copy packet data at set frequencies (e.g., every 10th or12th packet). While this sampling may not provide the most accuratepicture, it provides satisfactory results over longer periods of monitoring.
Top 8 Packet Sniffers
1. SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor
SolarWinds® Network Performance Monitor is an advanced network monitoring tool allowing you to monitor availability and security parameters with intelligent mapping, pre-configured dashboards, and advanced alerting features. With its network packet sniffer, you can get to the root cause of network issues and troubleshoot errors quickly. The tool identifies more than 1,200 applications, which makes it easier to analyze traffic and identify what’s leading to a poor end-user experience. It allows you to calculate response times for different applications, along with their data volume, and other performance indicators to categorize the traffic into different types and risk levels. You can use the Quality of Experience dashboard to get a holistic view of several metrics related to the network and application performance.
Network Performance Monitor also provides asimple visualization of traffic levels allowing you to identify any unusualspikes, which could be an indication of a security breach. While packetsniffing is one of the important features, Network Performance Monitor alsooffers several other advanced features, used by teams running networkoperations centers. With this tool, you can automate device discovery, performlatency tests, conduct network path analysis, implement SNMP monitoring, createWi-Fi heat maps, get visual traceroute from NetPath analysis, and more. Thetool can automatically poll a network for updates every five minutes. Itsautomated network alert feature helps in identifying critical issuesimmediately.
2. ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer
ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer is a comprehensive traffic analysis software capable of being installed on both Windows and Linux systems. It offers packet sniffing and passively monitors network sessions to extract details like IP addresses, host names, open ports, etc., without interfering with the data transmission. It offers a Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) add-on, which allows capturing packets from the network flows and analyzing the PCAP files. The add-on enables packet-level analysis to identify any application issues. It also includes granular visibility into bandwidth consumption across different applications in an enterprise network. IT teams can also monitor response times for troubleshooting purposes. Learn more about NetFlow Analyzer’s packet-sniffing capabilities here.
3. PRTG Network Monitor
PRTG Network Monitor is another popular network monitoring tool, designed to simplify packet capturing and analysis. It offers more than 200 sensors for monitoring different parts of a network. IT teams can make use of four core sensors viz Packet Sniffing, SFlow, NetFlow, and JFlow for sniffing IP packets. The sensors are designed to meet varied monitoring requirements; for instance, the packet sniffing sensor only captures packet headers and can be useful in monitoring traffic from emails, web servers, file transfers, and more. The SFlow sensor offers packet sampling, while NetFlow and JFlow sensors are designed for Cisco and Juniper devices, respectively. While the tool is easy to implement, you may have to install multiple sensors based on the size of your network, which also affects its pricing. You can learn more about the tool and its capabilities here.
4. Wireshark
Wireshark is a free and open-source packet analyzer tool, designed to support multiple platforms, including Windows, Linux, Solaris, FreeBSD, NetBSD, macOS, and more. In addition to connections using Ethernet, it can analyze live packet data from different types of networks, including Wireless LAN, USB, Bluetooth, and more. You can also send packet data from other packet sniffing programs to Wireshark for analysis. Deep inspection and decryption support for multiple protocols, powerful display filters, and offline analysis make Wireshark a highly useful tool for packet analysis and network monitoring. Being an open-source tool, it may pose certain challenges in configuration and upgrades; however, the tool is highly popular among network administrators, security engineers, QA teams, and developers. Simplify3d 4 1 1 x64 crack.
5. Tcpdump
Most system administrators are familiar withtcpdump, which is one of the oldest utilities for packet capturing. Thecommand-line utility works on Unix or Unix-like (Linux, Mac OS) operatingsystems, and can be installed for free. For Windows, you can install Windump,which performs similar to tcpdump. The packet capturing feature of tcpdump isavailable under the libpcab library. When the program is run, it startscapturing packets and displaying their contents. The program may keep runningforever until you specify a limit in advance or manually terminate the sessionwith a command. However, analyzing this data can be a complex task as one hasto learn several commands to filter and segment the data. This is why mostteams forward the packet data to tools like Wireshark to analyze the datacaptured by tcpdump.
6. OmniPeek Network Protocol Analyzer
Omnipeek Network Protocol Analyzer is a powerful monitoring tool offering advanced visualization, and quick resolution of network and application issues. It offers both flow-based and packet analysis features for real-time network analysis. The tool also supports Wi-Fi packet analysis; however, you’ll have to install various plugins to capture packets as the core software doesn’t offer packet sniffing. It can provide a detailed view of traffic by their protocol and throughput, using live charts and graphs. It also helps admins measure the transfer speeds and can raise threshold-based alerts. You can learn more about the tool and its advantages here.
7. NetworkMiner
NetworkMiner is another open-source tool used for packet sniffing and analysis. It’s a Windows-based tool but can also help in packet capturing on Linux, Mac OS X, and FreeBSD. With this tool, teams can perform passive network monitoring to keep track of sessions, hostnames, operating system, open ports, etc. without interfering with the network. It also identifies PCAP files for offline analysis. A highly intuitive user interface, faster processing, and open-source flexibility make NetworkMiner a popular tool among network administrators. You can learn more about the tool here.
8. Colasoft Caspa
Capsa is a simple network performance analysis and diagnostics tool, which can help you in real-time packet capturing and analysis. Its simple installation and a highly intuitive interface make it easier to implement. The application works on both LAN and WLAN networks and offers in-depth packet decoding. It offers a holistic view of the entire network, which helps administrators stay on top of their environment, detect issues, pinpoint the source of the error, and take remedial actions. The free version of the software can monitor up to 10 IP addresses but lacks several useful features. However, you’ll find the paid version highly useful for network security analysis.
Conclusion
Free Packet Sniffer Machine
We’ve discussed packet sniffing in detail and also covered some of the most popular packet sniffers used by IT teams around the world. Utilities like Tcpdump and Windump could be installed on all major platforms and support monitoring of network infrastructure. It’s possible to improve packet analysis further with tools like Wireshark. However, open-source tools can pose security and scalability challenges. For end-to-end monitoring of enterprise networks, system administrators have to rely on a wide range of monitoring techniques and tools. Installing open-source tools for every task can take up significant time and effort. This is why we recommend a commercial monitoring tools like SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor, which offers a free 30-day trial, so you can experience its multiple advanced features for comprehensive network analysis first hand.